Introduction
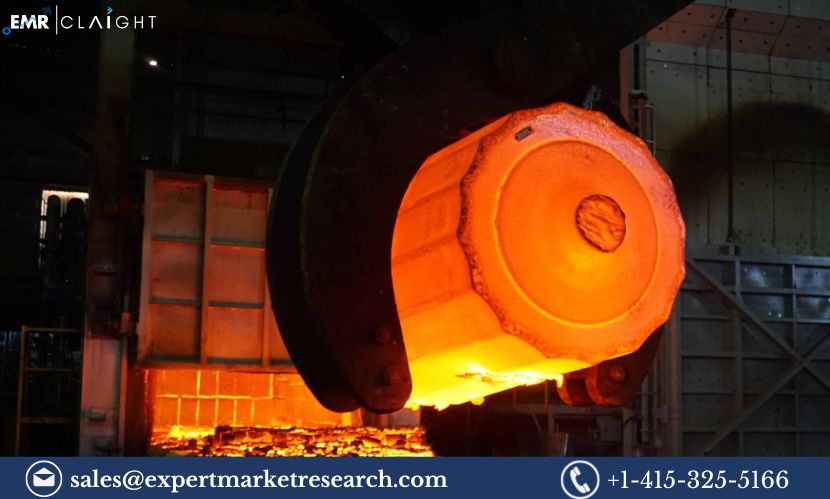
Steel forging is a critical manufacturing process in the production of high-strength components used across various industries, including automotive, aerospace, construction, and industrial machinery. Steel forgings are known for their superior mechanical properties, such as strength, durability, and resistance to fatigue, making them ideal for applications where performance and reliability are paramount. The demand for steel forgings has been steadily increasing due to industrial growth and the need for high-performance components. A Steel Forging Manufacturing Plant Project Report serves as a comprehensive guide for businesses or investors looking to establish a steel forging facility. This report outlines the process, machinery requirements, raw materials, market potential, and investment considerations for setting up a steel forging manufacturing plant.
Market Demand for Steel Forging
Steel forgings are utilized in many sectors that require high-strength, reliable, and durable parts. The following factors contribute to the growing demand for steel forging:
-
Automotive Industry: With the increasing production of high-performance vehicles, steel forgings are extensively used in critical engine components, transmission parts, and structural elements.
-
Aerospace: Aerospace manufacturers use steel forgings for components that must withstand extreme temperatures and stresses, such as turbine blades, landing gears, and structural frames.
-
Construction and Infrastructure: Steel forgings are used for heavy-duty components in construction machinery, bridges, and structural elements that require superior strength.
-
Oil and Gas: Steel forgings are used in the oil and gas industry for drilling equipment, valves, and pumps, where corrosion resistance and high strength are crucial.
As global infrastructure projects expand and technological advancements continue, the demand for high-quality forged steel products is expected to grow.
Get a Free Sample Report with Table of Contents@
Industry Overview
Global Steel Forging Market Trends
The global steel forging market has seen significant growth due to the increasing demand for stronger and more durable components in industrial applications. Key trends influencing the steel forging market include:
-
Technological Advancements: Innovations in forging processes, such as closed-die forging and precise forging techniques, have enhanced the quality and precision of forged steel parts. These advances allow for the production of more complex and high-performance components.
-
Increasing Demand for High-Strength Steel: The rise of industries requiring lightweight, high-strength materials, such as automotive and aerospace, has driven the demand for superior quality steel forgings.
-
Automated and Lean Manufacturing: Manufacturers are adopting automation technologies in the forging process to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and ensure consistent product quality.
-
Sustainability and Environmental Concerns: As with many other industries, there is an increasing focus on reducing the carbon footprint of steel production and forging processes, which has led to the adoption of energy-efficient methods and recycling techniques.
In 2020, the global steel forging market was valued at USD 45 billion and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 5% from 2021 to 2028. This continued growth presents lucrative opportunities for new businesses entering the steel forging market.
Applications of Steel Forging
Steel forgings find application in a wide variety of industries, including:
-
Automotive Components: Forged steel parts are used in engine blocks, crankshafts, gears, and suspension components due to their ability to withstand high stress and fatigue.
-
Aerospace: Components such as turbine blades, engine components, and landing gears are made from forged steel for their high strength and resistance to temperature fluctuations.
-
Heavy Machinery: Forged steel parts are used in construction and mining machinery, including gears, shafts, and hydraulic components.
-
Oil & Gas: The oil and gas industry uses forged steel for valves, pumps, and drilling equipment that must endure high pressures and corrosive environments.
-
Defense and Military: Steel forgings are used in weapons systems, armored vehicles, and structural components in military equipment.
Steel Forging Manufacturing Process
Steel forging involves the shaping of steel using compressive forces to produce a part that has superior mechanical properties compared to castings. The process requires precision, skilled labor, and specialized equipment. Here is an overview of the steel forging process:
1. Material Selection and Heating
The forging process begins with selecting the appropriate grade of steel based on the requirements of the final product. The steel is then heated in a furnace to the proper temperature, typically between 1100°C to 1300°C, depending on the type of steel being used. The steel must reach a high temperature to become malleable and easy to shape.
2. Forging
Once the steel reaches the desired temperature, it is transferred to the forging press or hammer for shaping. There are two main types of forging processes:
-
Open-Dye Forging: In this process, the steel is placed between two dies, and pressure is applied to shape the material. This process is ideal for simpler shapes and parts with low to medium production volumes.
-
Closed-Dye Forging: In this method, the steel is placed between precisely shaped dies that control the material’s flow. This method is used for complex parts and provides higher accuracy and better material properties. Closed-die forging is more commonly used for high-volume production.
The forging press or hammer applies extreme force to the steel, which allows the material to be shaped and compressed into the desired form.
3. Cooling and Normalizing
After the forging process, the hot steel is allowed to cool. It is often subjected to a normalizing process, where it is heated again to a specific temperature and then cooled in air. This helps to refine the grain structure and improve the mechanical properties of the forged steel.
4. Machining
Once the steel has cooled and stabilized, the forged components often require additional machining to achieve precise dimensions. This step may involve cutting, drilling, turning, and grinding to ensure the part meets the required specifications.
-
CNC Machining: Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machines are often used for precise machining and to achieve complex geometries in forged components.
5. Heat Treatment
To further enhance the mechanical properties of the forged steel, it may undergo heat treatment processes such as quenching and tempering. These treatments improve hardness, toughness, and tensile strength, which are critical for parts used in high-stress applications.
6. Surface Finishing
After heat treatment, the forged parts may undergo a surface finishing process to improve their appearance and resistance to wear and corrosion. Common finishing techniques include:
-
Shot Blasting: To clean the surface and remove any oxide scales.
-
Coating: For additional protection against rust and wear, coatings such as galvanizing or painting may be applied.
7. Quality Control
Throughout the manufacturing process, quality control is essential to ensure that each forged component meets the required specifications. Common quality checks include:
-
Dimensional Inspection: Ensuring the part’s dimensions match the required tolerances.
-
Mechanical Testing: Testing for strength, toughness, and fatigue resistance using techniques such as tensile testing and hardness testing.
-
Visual Inspection: Checking for surface defects such as cracks or inclusions.
8. Packaging and Distribution
Once the steel forgings have passed all quality checks, they are carefully packaged for distribution. Proper packaging is essential to avoid damage during transit. The forged components are then shipped to customers in various industries.
Plant Setup and Investment
Location Selection
Choosing the right location for a steel forging manufacturing plant is crucial for cost-effectiveness and operational efficiency. Factors to consider include:
-
Proximity to Raw Material Suppliers: Being close to steel suppliers and other raw materials such as alloys can help reduce transportation costs.
-
Skilled Workforce: A location with access to skilled labor in metallurgy, engineering, and machining is vital for ensuring the production of high-quality forged steel components.
-
Infrastructure: Availability of transportation networks, energy supply, and water resources is crucial for smooth plant operations.
Equipment and Machinery
Key equipment required for steel forging includes:
-
Furnaces: For heating steel to the required forging temperature.
-
Forging Presses: Hydraulic, mechanical, or pneumatic presses used to shape the steel.
-
Hammers: Used for manual or automated forging operations.
-
CNC Machines: For machining the forged parts to precise dimensions.
-
Heat Treatment Equipment: For controlled heating and cooling processes.
-
Surface Finishing Equipment: Such as shot blasters, grinders, and coating machines.
Investment and Operational Costs
Setting up a steel forging plant requires a substantial investment in equipment, infrastructure, and working capital. Major costs include:
-
Facility Construction: Building the plant, including foundations, floors, and specialized rooms for equipment.
-
Machinery and Equipment: Purchasing and installing forging presses, CNC machines, furnaces, and finishing equipment.
-
Raw Materials: Procuring steel billets, alloys, and other raw materials.
-
Labor: Hiring skilled workers, engineers, and technical staff.
-
Utilities: Power and water consumption for heating and cooling processes.
Regulatory Compliance
The steel forging industry is subject to various regulations to ensure safety, environmental protection, and product quality. Key regulatory requirements include:
-
Environmental Regulations: Compliance with air and water pollution controls, waste management, and energy consumption standards.
-
Safety Standards: Adherence to safety protocols for the handling of hot metals and the operation of heavy machinery.
-
Quality Certifications: Obtaining ISO and other quality management certifications to ensure product reliability and consistency.
Financial Projections and Market Analysis
A Steel Forging Manufacturing Plant Project Report should include detailed financial projections that assess the potential return on investment (ROI). The report should cover:
-
Initial Capital Investment: Breakdown of costs for land, building, machinery, and raw materials.
-
Revenue Projections: Based on market demand, pricing, and expected production volume.
-
Operational Costs: Ongoing costs for labor, utilities, raw materials, and maintenance.
-
Profitability Analysis: Estimation of profits and ROI over a 5-10 year period.
https://www.expertmarketresearch.com/blogs/top-pallet-companies-in-united-states
https://www.expertmarketresearch.com/blogs/top-ammunition-manufacturers
https://www.expertmarketresearch.com/blogs/top-concrete-companies-in-saudi-arabia