Introduction to Varicocele Embolisation
Varicocele, an enlargement of the veins within the scrotum, is a common condition that affects a significant percentage of men. It is often linked to male infertility, as it can interfere with sperm production and quality. While there are various treatments available for varicocele, one of the most effective and minimally invasive options is varicocele embolisation.
In this article, we will explore what varicocele embolisation is, how it works, the benefits, and potential risks associated with the procedure. If you’re considering treatment for varicocele, this guide will help you make an informed decision.
What is Varicocele?
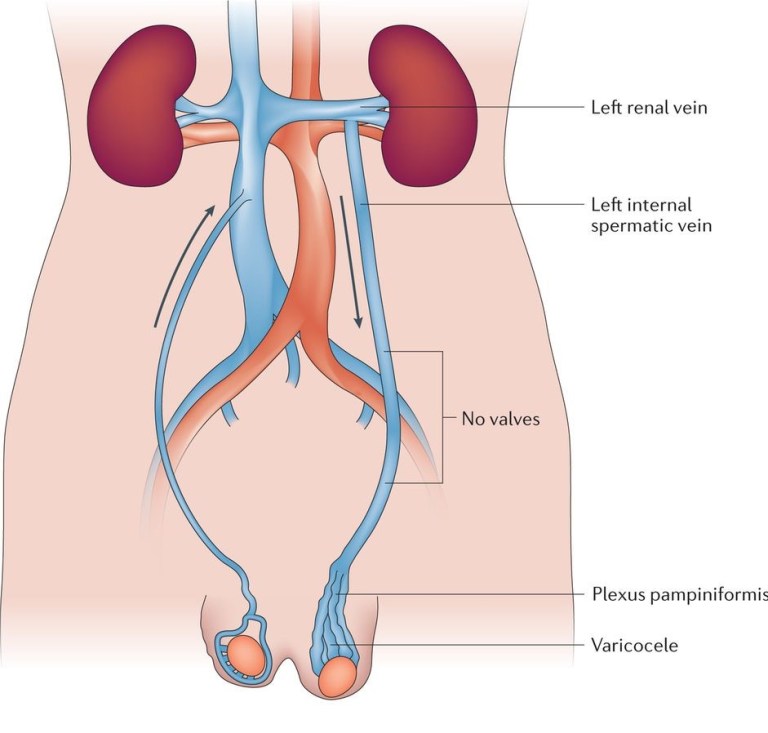
Before diving into the specifics of varicocele embolisation, it’s essential to understand what varicocele is. A varicocele occurs when the veins in the scrotum, known as the pampiniform plexus, become enlarged. These veins are responsible for draining blood from the testicles, but when they become dilated, they can hinder proper blood flow and lead to a rise in temperature around the testicles. This increase in temperature can impair sperm production and quality, potentially causing fertility issues.
Varicoceles are often asymptomatic but may cause discomfort or swelling in some cases. They are typically diagnosed during a physical exam, and if infertility or other complications are present, treatment may be necessary.
What is Varicocele Embolisation?
Varicocele embolisation is a non-surgical, minimally invasive procedure used to treat varicoceles. Unlike traditional surgical methods such as varicocelectomy, embolisation does not require an incision, making it a preferred option for many patients. The procedure involves blocking off the enlarged veins to restore normal blood flow and prevent further damage to the testicles.
The procedure is performed by a specialist known as an interventional radiologist. It is typically done under local anesthesia, and patients can usually return to their normal activities within a few days.
How Does Varicocele Embolisation Work?
During the varicocele embolisation procedure, a small catheter is inserted into a vein, usually through the groin or neck area. The catheter is guided to the affected veins in the scrotum using real-time X-ray imaging. Once the catheter reaches the targeted area, the interventional radiologist will inject a special embolic agent, such as coils or a gel-like substance, to block off the enlarged veins.
By blocking the problematic veins, blood flow is rerouted to healthier veins, and the varicocele is effectively treated. This helps reduce pressure in the affected veins and restores normal circulation to the testicles.
Benefits of Varicocele Embolisation
Varicocele embolisation offers several advantages over traditional surgical treatments:
-
Minimally Invasive: One of the main benefits of embolisation is that it is minimally invasive. There are no large incisions required, which means a quicker recovery time and minimal scarring.
-
Quick Recovery: Most patients can resume normal activities within a few days after the procedure. While there may be some mild discomfort, it typically resolves within a short period.
-
High Success Rate: Studies have shown that varicocele embolisation has a high success rate in treating varicoceles and improving fertility. The procedure has a low recurrence rate, meaning that the varicocele is unlikely to return after treatment.
-
No Need for General Anesthesia: Since the procedure is performed under local anesthesia, there is no need for general anesthesia, which reduces the risks and complications associated with surgery.
-
Effective for Pain Relief: In addition to treating infertility, varicocele embolisation can also provide relief from pain and discomfort caused by varicoceles. Many patients experience significant improvement in their symptoms after the procedure.
Risks and Potential Complications
Like any medical procedure, varicocele embolisation does come with some risks. However, the risks are generally minimal, especially when performed by an experienced interventional radiologist.
Potential risks and complications include:
- Infection: As with any procedure involving a catheter, there is a small risk of infection at the insertion site.
- Bleeding: Although rare, bleeding can occur during or after the procedure.
- Allergic Reaction: Some patients may have an allergic reaction to the contrast dye used during the procedure.
- Recurrence: While the success rate of varicocele embolisation is high, in some cases, the varicocele may return after a period of time.
- Discomfort or Swelling: Mild discomfort, swelling, or bruising at the catheter insertion site is common but typically resolves quickly.
It’s important to discuss these risks with your doctor to ensure you have a full understanding of the procedure.
Who is a Good Candidate for Varicocele Embolisation?
Varicocele embolisation is suitable for most men with varicoceles, especially those who experience infertility or discomfort related to the condition. It is typically recommended for individuals who:
- Have been diagnosed with a varicocele.
- Have symptoms such as pain, swelling, or infertility related to the varicocele.
- Do not want to undergo traditional surgical methods.
- Are in good overall health and do not have any contraindications to the procedure.
Your doctor will assess your medical history and symptoms to determine whether varicocele embolisation is the best treatment option for you.
The Procedure: What to Expect
The varicocele embolisation procedure typically takes about 30 minutes to an hour. Here’s a step-by-step overview of what you can expect:
- Preparation: You will be asked to lie down on a procedure table, and the area where the catheter will be inserted will be cleaned and sterilized.
- Local Anesthesia: Local anesthesia will be applied to numb the area where the catheter will be inserted.
- Insertion of the Catheter: The interventional radiologist will make a small incision and insert a catheter into a vein, usually in the groin or neck area.
- Embolisation: Once the catheter is positioned near the varicocele, the radiologist will inject an embolic agent to block the affected veins.
- Post-Procedure Care: After the procedure, you will be monitored for a short period before being allowed to go home the same day.
Recovery and Aftercare
One of the major benefits of varicocele embolisation is the minimal downtime required for recovery. Most patients experience mild discomfort for a day or two, but this usually resolves quickly. It’s recommended to avoid strenuous physical activity for a week or so, but most men can return to work and other regular activities within a few days.
Follow-up visits may be scheduled to monitor your progress and ensure that the varicocele has been successfully treated.
How Long Does It Take to See Results?
Patients often experience significant improvements in fertility and symptoms within a few months of undergoing varicocele embolisation. It may take some time for sperm count and quality to improve, so it’s important to follow your doctor’s advice and be patient with the process.
Conclusion
Varicocele embolisation is a safe, effective, and minimally invasive treatment option for men with varicoceles, particularly those struggling with infertility or discomfort. The procedure offers several benefits, including a quick recovery time, high success rate, and minimal risk of complications.
If you’re considering treatment for varicocele, speak to a healthcare provider who specializes in interventional radiology to determine whether varicocele embolisation is right for you. With the right care and treatment, you can expect relief from symptoms and an improvement in your fertility.